
By Jenny Whilde and Jessica Alice Farrell
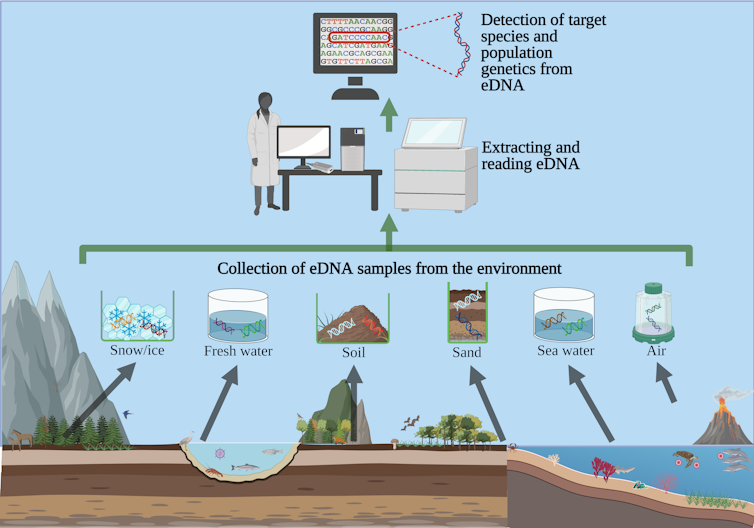
Human DNA can be sequenced from small amounts of water, sand and air in the environment to potentially extract identifiable information like genetic lineage, gender, and health risks, according to our new research.
Every cell of the body contains DNA. Because each person has a unique genetic code, DNA can be used to identify individual people. Typically, medical practitioners and researchers obtain human DNA through direct sampling, such as blood tests, swabs or biopsies. However, all living things, including animals, plants and microbes, constantly shed DNA. The water, soil and even the air contain microscopic particles of biological material from living organisms.
DNA that an organism has shed into the environment is known as environmental DNA, or eDNA. For the last couple of decades, scientists have been able to collect and sequence eDNA from soil or water samples to monitor biodiversity, wildlife populations and disease-causing pathogens. Tracking rare or elusive endangered species through their eDNA has been a boon to researchers, since traditional monitoring methods such as observation or trapping can be difficult, often unsuccessful and intrusive to the species of interest.
Researchers using eDNA tools usually focus only on the species they’re studying and disregard DNA from other species. However, humans also shed, cough and flush DNA into their surrounding environment. And as our team of geneticists, ecologists and marine biologists in the Duffy Lab at the University of Florida found, signs of human life can be found everywhere but in the most isolated locations.
Animals, humans and viruses in eDNA
Our team uses environmental DNA to study endangered sea turtles and the viral tumors to which they are susceptible. Tiny hatchling sea turtles shed DNA as they crawl along the beach on their way to the ocean shortly after they are born. Sand scooped from their tracks contains enough DNA to provide valuable insights into the turtles and the chelonid herpesviruses and fibropapillomatosis tumors that afflict them. Scooping a liter of water from the tank of a recovering sea turtle under veterinary care equally provides a wealth of genetic information for research. Unlike blood or skin sampling, collecting eDNA causes no stress to the animal.
Genetic sequencing technology used to decode DNA has improved rapidly in recent years, and it is now possible to easily sequence the DNA of every organism in a sample from the environment. Our team suspected that the sand and water samples we were using to study sea turtles would also contain DNA from a number of other species – including, of course, humans. What we didn’t know was just how informative the human DNA we could extract would be.

Todd Osborne, CC BY-ND
To figure this out, we took samples from a variety of locations in Florida, including the ocean and rivers in urban and rural areas, sand from isolated beaches and a remote island never usually visited by people. We found human DNA in all of those locations except the remote island, and these samples were high quality enough for analysis and sequencing.
We also tested the technique in Ireland, tracing along a river that winds from a remote mountaintop, through small rural villages and into the sea at a larger town of 13,000 inhabitants. We found human DNA everywhere but in the remote mountain tributary where the river starts, far from human habitation.
We also collected air samples from a room in our wildlife veterinary hospital in Florida. People who were present in the room gave us permission to take samples from the air. We recovered DNA matching the people, the animal patient and common animal viruses present at the time of collection.
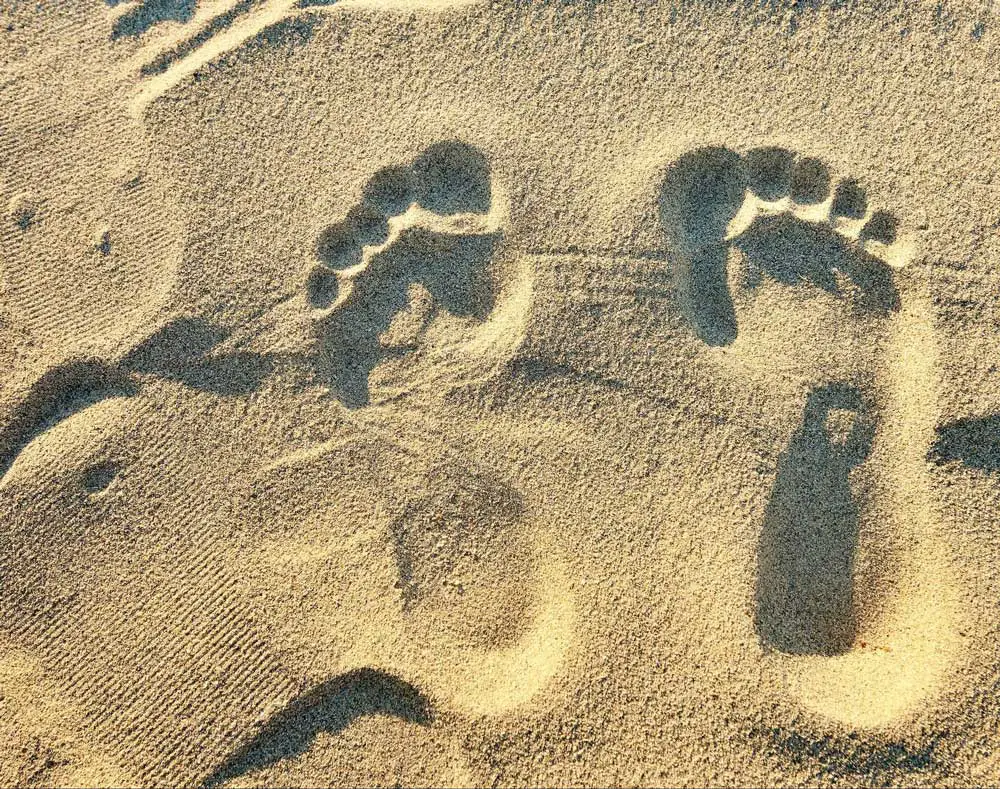
Surprisingly, the human eDNA found in the local environment was intact enough for us to identify mutations associated with disease and to determine the genetic ancestry of people who live in the area. Sequencing DNA that volunteers left in their footprints in the sand even yielded part of their sex chromosomes.
Liam Whitmore/Created with BioRender.com, CC BY-NC-ND
Ethical implications of collecting human eDNA
Our team dubs inadvertent retrieval of human DNA from environmental samples “human genetic bycatch.” We’re calling for deeper discussion about how to ethically handle human environmental DNA.
Human eDNA could present significant advances to research in fields as diverse as conservation, epidemiology, forensics and farming. If handled correctly, human eDNA could help archaeologists track down undiscovered ancient human settlements, allow biologists to monitor cancer mutations in a given population or provide law enforcement agencies useful forensic information.

David Duffy, CC BY-ND
However, there are also myriad ethical implications relating to the inadvertent or deliberate collection and analysis of human genetic bycatch. Identifiable information can be extracted from eDNA, and accessing this level of detail about individuals or populations comes with responsibilities relating to consent and confidentiality.
While we conducted our study with the approval of our institutional review board, which ensures that studies on people adhere to ethical research guidelines, there is no guarantee that everyone will treat this type of information ethically.
Many questions arise regarding human environmental DNA. For instance, who should have access to human eDNA sequences? Should this information be made publicly available? Should consent be required before taking human eDNA samples, and from whom? Should researchers remove human genetic information from samples originally collected to identify other species?
We believe it is vital to implement regulations that ensure collection, analysis and data storage are carried out ethically and appropriately. Policymakers, scientific communities and other stakeholders need to take human eDNA collection seriously and balance consent and privacy against the possible benefits of studying eDNA. Raising these questions now can help ensure everyone is aware of the capabilities of eDNA and provide more time to develop protocols and regulations to ensure appropriate use of eDNA techniques and the ethical handling of human genetic bycatch.
![]()
Jenny Whilde is an Adjunct Research Scientist in Marine Bioscience at the University of Florida. Jessica Alice Farrell is a Postdoctoral associate at the University of Florida.





























Pogo says
@Finally
The answer to the question: Who cut the cheese?
Jimbo99 says
I would think that eDNA would be used for crimes without any ethical issues as it pertains to a criminal. Outside of that, who cares who went to the beach or a park and just lived their best lives. Not much monetization of eDNA in that ? Those brokering in eDNA data become fabulously wealthy for eDNA to others like data is bought & sold already. The effort to collect and link eDNA to the actual crime would be something they would have to have an extensive database of 330 million Americans, let alone the 8 billion & growing global population, in place to compare samples recovered vs what’s “on file”. Just from a purely scientific perspective ?
Laurel says
Right now, scientists need permission to study an individual’s DNA, except in criminal cases. For instance, if you sign up for 23 and Me, you are already giving consent. To be a part of Tapestry, I had to sign a consent form. How does anyone get permission from an already sourced eDNA sample? Permission will be a thing of the past. So, it’s the same story about responsibility. Will the lab inform you that you are susceptible for breast cancer? They will know if you like cilantro or not. The future is great, and creepy.