By Deborah Fuller
The two most successful coronavirus vaccines developed in the U.S. – the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines – are both mRNA vaccines. The idea of using genetic material to produce an immune response has opened up a world of research and potential medical uses far out of reach of traditional vaccines. Deborah Fuller is a microbiologist at the University of Washington who has been studying genetic vaccines for more than 20 years. We spoke to her about the future of mRNA vaccines for The Conversation Weekly podcast.
Below are excerpts from that conversation which have been edited for length and clarity.
How long have gene-based vaccines been in development?
This type of vaccine has been in the works for about 30 years. Nucleic acid vaccines are based on the idea that DNA makes RNA and then RNA makes proteins. For any given protein, once we know the genetic sequence or code, we can design an mRNA or DNA molecule that prompts a person’s cells to start making it.
When we first thought about this idea of putting a genetic code into somebody’s cells, we were studying both DNA and RNA. The mRNA vaccines did not work very well at first. They were unstable and they caused pretty strong immune responses that were not necessarily desirable. For a very long time DNA vaccines took the front seat, and the very first clinical trials were with a DNA vaccine.
But about seven or eight years ago, mRNA vaccines started to take the lead. Researchers solved a lot of the problems – notably the instability – and discovered new technologies to deliver mRNA into cells and ways of modifying the coding sequence to make the vaccines a lot more safe to use in humans.
Once those problems were solved, the technology was really poised to become a revolutionary tool for medicine. This was just when COVID-19 hit.
What makes nucleic acid vaccines different from traditional vaccines?
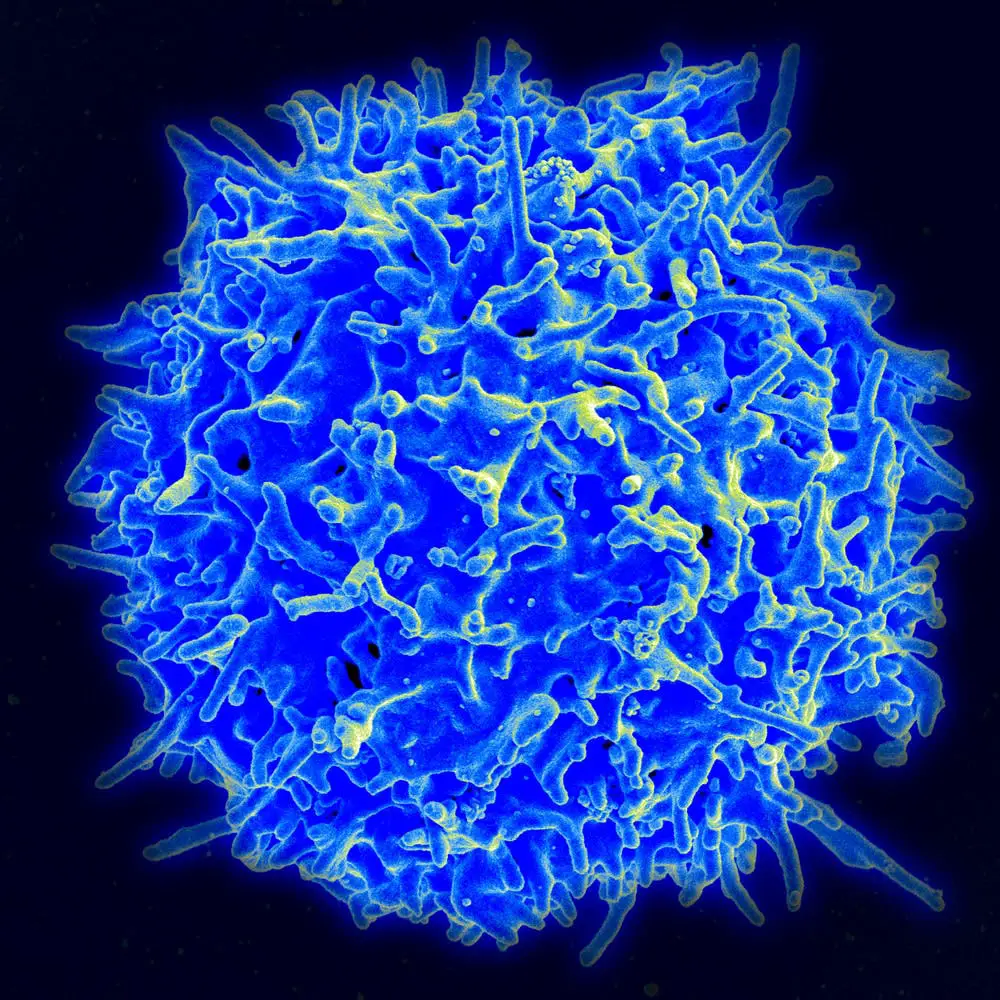
Most vaccines induce antibody responses. Antibodies are the primary immune mechanism that blocks infections. As we began to study nucleic acid vaccines, we discovered that because these vaccines are expressed within our cells, they were also very effective at inducing a T cell response. This discovery really prompted additional thinking about how researchers could use nucleic acid vaccines not just for infectious diseases, but also for immunotherapy to treat cancers and chronic infectious diseases – like HIV, hepatitis B and herpes – as well as autoimmune disorders and even for gene therapy.
How can a vaccine treat cancers or chronic infectious diseases?
T cell responses are very important for identifying cells infected with chronic diseases and aberrant cancer cells. They also play a big role in eliminating these cells from the body.
When a cell becomes cancerous, it starts producing neoantigens. In normal cases, the immune system detects these neoantigens, recognizes that something’s wrong with the cell and eliminates it. The reason some people get tumors is that their immune system isn’t quite capable of eliminating the tumor cells, so the cells propagate.
With an mRNA or DNA vaccine, the goal is to make your body better able to recognize the very specific neoantigens the cancer cell has produced. If your immune system can recognize and see those better, it will attack the cancer cells and eliminate them from the body.
This same strategy can be applied to the elimination of chronic infections like HIV, hepatitis B and herpes. These viruses infect the human body and stay in the body forever unless the immune system eliminates them. Similar to the way nucleic acid vaccines can train the immune system to eliminate cancer cells, they can be used to train our immune cells to recognize and eliminate chronically infected cells.
What is the status of these vaccines?
Some of the very first clinical trials of nucleic acid vaccines happened in the 1990s and were for cancer, particularly for melanoma.
Today, there are a number of ongoing mRNA clinical trials for the treatment of melanoma, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, leukemia, glioblastoma and others, and there have been some promising outcomes. Moderna recently announced promising results with its phase 1 trial using mRNA to treat solid tumors and lymphoma
There are also a lot of ongoing trials looking at cancer DNA vaccines, because DNA vaccines are particularly effective in inducing T cell responses. A company called Inovio recently demonstrated a significant impact on cervical cancer caused by human papilloma virus in women using a DNA vaccine.
Can nucleic acid vaccines treat autoimmune disorders?
Autoimmune disorders occur when a person’s immune cells are actually attacking a part of the person’s own body. An example of this is multiple sclerosis. If you have multiple sclerosis, your own immune cells are attacking myelin, a protein that coats the nerve cells in your muscles.
The way to eliminate an autoimmune disorder is to modulate your immune cells to prevent them from attacking your own proteins. In contrast to vaccines, whose goal is to stimulate the immune system to better recognize something, treatment for autoimmune diseases seeks to dampen the immune system so that it stops attacking something it shouldn’t. Recently, researchers created an mRNA vaccine encoding a myelin protein with slightly tweaked genetic instructions to prevent it from stimulating immune responses. Instead of activating normal T cells that increase immune responses, the vaccine caused the body to produce T regulatory cells that specifically suppressed only the T cells that were attacking myelin.
Any other applications of the new vaccine technology?
The last application is actually one of the very first things that researchers thought about using DNA and mRNA vaccines for: gene therapy. Some people are born missing certain genes. The goal with gene therapy is to supply cells with the missing instructions they need to produce an important protein.
A great example of this is cystic fibrosis, a genetic disease caused by mutations in a single gene. Using DNA or an mRNA vaccine, researchers are investigating the feasibility of essentially replacing the missing gene and allowing someone’s body to transiently produce the missing protein. Once the protein is present, the symptoms could disappear, at least temporarily. The mRNA would not persist very long in the human body, nor would it integrate into people’s genomes or change the genome in any way. So additional doses would be needed as the effect wore off.
Research has shown that this concept is feasible, but it still needs some work.
![]()
Deborah Fuller is Professor of Microbiology at the School of Medicine, University of Washington.
![]()
![]()





























Jimbo99 says
Hmmmm, doesn’t keep anyone from getting Covid, just males sense that it should prevent Cancer & any other diseases too ? Sounds like they’re anchoring in a mRNA shot for everything.
Ray W. says
About 10 years ago, French researchers posed the idea that genetically modified HIV-based viral organisms might provide an effective cancer treatment, provided researchers could produce a form of modification that would target blood cancer cells. Once researchers were successful in producing that particularized form of viral organism, the theory was put into practice in America at a Philadelphia hospital, where a team treated a child who suffered from leukemia to the point that the cancer required hospice care, as all other known treatments had proved ineffective. As the modified HIV viral organisms multiply rapidly during the process of killing leukemia cells, when the organisms were introduced into the child’s bloodstream, they killed so many leukemia-cancer cells so rapidly that the child nearly died from the treatment, but she recovered. When I first read about this novel treatment regimen, my recollection is that the article detailed that some six pounds of dead leukemia cells were extracted from her blood during dialysis. The treatment has been used since in both children and adults, but it is still considered an experimental treatment regimen, though many hospitals worldwide are now using the procedure. All with great success, though not universal success. Early studies show an 80% remission rate, which is phenomenal considering the seriousness of the stage of the illness when the treatment is instituted.
Something tells me that Jimbo99 is caught in a trap of conspiratorial thinking and can’t quite grasp the fact that advances in medical science can transfer across many fields of medical treatment. Of course, I am old enough to remember the first trial in Volusia County, in which my supervisor at the time, Peter Marshall, successfully argued to the trial judge that DNA test results were sufficiently reliable to be admitted into evidence. In those days, the available technology took many days to complete each test and costs ran into the thousands of dollars for just one test, which used “molecular scissors” to cut up DNA strands that were placed in a gel and drawn across the gel over time. The larger strands traveled more slowly, creating a “fingerprint” of strands that could be compared to a standard. Today, the costs and time needed to complete a DNA test has plummeted, using STR (short tandem repeat) technology to multiply DNA at certain locations on the strand, which leaves a different type of fingerprint that is compared to standards. What was once considered nearly miraculous and expensive is now commonplace and cheap. All Jimbo99 has to do is envision life before the Wright brothers first planned to build an airplane. If Jimbo99 is capable of envisioning that time, and then picture just how far the aviation field has progressed, then he should also be able to easily envision the pioneering nature of the technology behind mRNA and, perhaps, even see the potential benefits that might spread across multiple medical disciplines, benefits that a future generation might see as commonplace.
I accept that there will always be those among us who envision a natural treatment for every disease. Some of the natural treatment crowd will always reject what they term as “synthetic” treatments. And there is little doubt in my mind that natural treatments, combined with a healthy lifestyle and healthy eating habits can cure many illnesses. The idea behind Prevention magazine, so popular long before my birth and still popular today, was based on the use of natural remedies, coupled with healthy eating and living habits. In my father’s generation, it was a common belief that hospitals were the place one went to die. I suspect that this mindset triggers the anti-vaxxers among us to grasp onto any proposed “natural” treatment regimen, such as, in their view, monoclonal antibodies, as superior to any “synthetic” treatment regimen, such as vaccines. What was once considered miraculous, such as when widespread acceptance of certain vaccines led to the eradication of polio and smallpox, is now considered commonplace, which may be one reason why the covid vaccines are so easily dismissed by anti-vaxxers.
Deborah Coffey says
I don’t know why FlaglerLive is allowing you to put false information into print!
FlaglerLive says
Jimbo’s comment is a ridiculous observation but he’s not stating anything factual, or factually false. Many of his comments are held back for attempting top spread misinformation, however.
Steve says
OH Thee of such little Faith Welcome to the 21st Century thing s are going to be different
cgm says
a 3rd vaccine was developed in the US that was just as effective but the Big Pharma did want to use it because it couldn’t be patented. It was 90% effective and made the same way the hep C vaccine is made, and it only cost $1.00 to $1.50 per dose.
It is being used outside the US.
Bill C says
One part ivermectin, one part hydroxychloroquine, one part bleach, add ice, shake and serve.
Pogo says
@And its name is CORBEVAX
https://www.google.com/search?q=CORBEVAX
CORBEVAX, a new patent-free COVID-19 vaccine, could be a pandemic game changer globally
https://theconversation.com/corbevax-a-new-patent-free-covid-19-vaccine-could-be-a-pandemic-game-changer-globally-174672