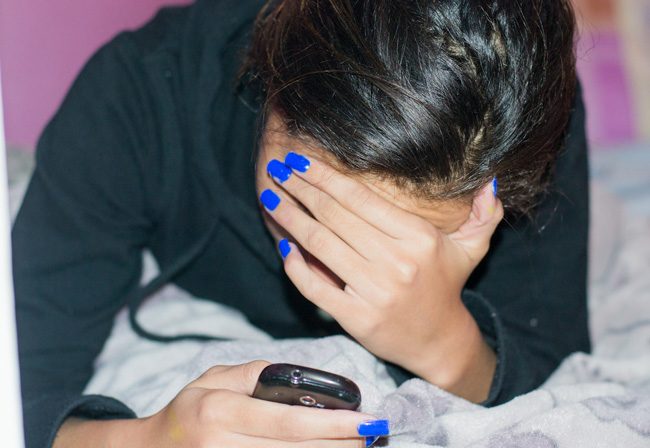

With one judge pointing to a lack of “sufficient maturity to make this critical decision,” a state appeals court Monday rejected a minor’s attempt to get an abortion without her parents being notified.
A three-judge panel of the 1st District Court of Appeal upheld an Escambia County circuit judge’s decision to refuse to grant a waiver from the state’s parental-notification law. The ruling did not detail the age or the hometown of the minor, identifying her only as “Jane Doe 16-A.”
Florida voters in 2004 approved a constitutional amendment that requires parents to be notified before their minor daughters can have abortions. But that amendment and subsequent laws created a process for minors to go to court to prevent the notification — a process known as a judicial bypass or waiver.
Monday’s ruling said the minor based her request on two legal grounds: that she was sufficiently mature to decide whether to have the abortion and that the notification would not be in the “best interests of the petitioner.”
In a four-page opinion written by Chief Judge Clay Roberts and joined by judges M. Kemmerly Thomas and Scott Makar, the appeals court said it could find “no abuse of discretion” in Escambia County Circuit Judge Coleman Lee Robinson’s decision to reject a waiver from the notification requirement.
“In considering the denial of a petition for judicial waiver, this court looks to whether the circuit court abused its discretion and may not reweigh the evidence presented below in order to reach a different result from the circuit court,” Roberts wrote. “Our review on appeal is highly deferential to the circuit court, due, in large part, to the confidential, non-adversarial nature of the proceeding below. The circuit court sits in a far better position to assess a minor’s demeanor and credibility than this court can upon review of the transcribed hearing.”
Makar wrote a more-detailed concurring opinion, saying that the minor’s testimony “fell short of the clear and convincing standard required to obtain a judicial order that her parents not be notified she is seeking to terminate her pregnancy.”
“Among many evidentiary deficiencies, the minor did not know what the medical procedure involved (and had no plan if post-surgical complications arose), had accepted little or no responsibility for ‘anything at all’ in her life, and planned on her parents paying for the procedure,” Makar wrote. “The limited evidentiary record paints a portrait of an emotionally overwhelmed young woman lacking sufficient maturity to make this critical decision independent of her parents for whom she expressed only a generalized fear about their possible reaction.”
The ruling does not prevent the minor from having an abortion but requires that a physician notify her parents before it can be performed.
The parental-notification law has been controversial, but a footnote in Makar’s concurring opinion suggested that judges rarely turn down requests for waivers. The footnote said 89.5 percent of petitions were granted in 2013, 90.5 percent in 2014 and 94.7 percent in 2015.




























Leave a Reply