
By Mireille Rebeiz
Lebanese families have been fleeing the country’s south in the thousands amid escalating tensions and an Israeli bombardment that has so far killed hundreds.
Their fear, echoed by many onlookers, is that Israel will accompany the airstrikes with something that has the potential to have far worse consequences: a ground invasion of south Lebanon.
The rational behind such a move, from the Israeli government’s perspective, is that a ground offensive may be its best chance to push Hezbollah fighters beyond the Litani River in the middle of the country. This would achieve an Israeli war goal of securing its northern borders and allowing an estimated 60,000 residents who have been forced to flee northern Israel to go back to their homes.
Irrespective of motive, a ground invasion and potential occupation is more than wild speculation. Israel has placed thousands of soldiers on standby close to the Lebanon border for such an eventuality.
Nor is such a move without precedent.
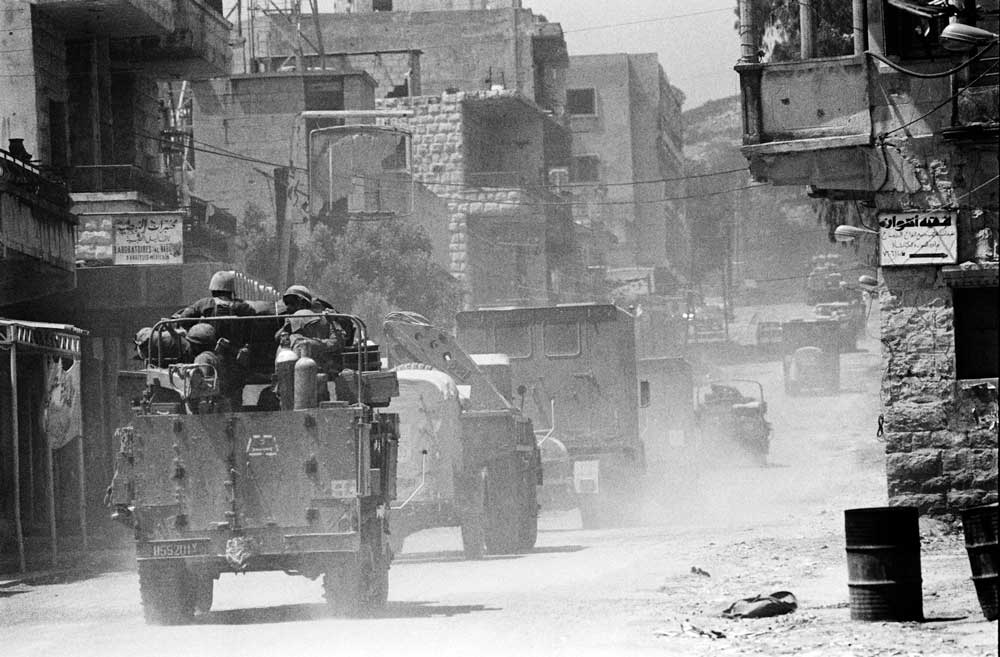
As a scholar of Lebanese history, I know Israel and Lebanon have been here before. In 1982, Israel invaded Lebanon in the middle of the latter’s civil war, imposing a siege on the capital Beirut. The results were catastrophic for the whole region. Not only did the ground invasion result in the death of thousands of civilians, the occupation of Lebanon plunged an already fragile nation into lasting political and economic chaos and led to the birth of Hezbollah, the very group that threatens northern Israel today.
Refuge and armed resistance
The Israeli invasion of Lebanon in June 1982 had its roots in the Palestinian–Israeli conflict, much as the fighting between Hezbollah and Israel does today.
The creation of the state of Israel in 1948 was accompanied by the Nakba, or “catastrophe,” for the Palestinians. In the violent birth pangs of a Jewish state on land inhabited by, among others, Arab populations with deep ancestral ties to villages, more than 750,000 Palestinians were expelled or fled.
Many refugees entered Lebanon, where in 1964 the Palestine Liberation Organization was born. By the mid-1970s, the armed resistance group had recruited and trained over 20,000 fighters who actively participated in launching attacks on Israel from Lebanese soil.
By 1982, Lebanon was already seven years into its civil war, with violence flaring between Lebanese Christians and Lebanese and Palestinian Muslims. On June 6, 1982, Israeli Defense Minister Ariel Sharon, a future leader of the country, launched Operation Peace for Galilee and invaded Lebanon with the purpose of eliminating the PLO.
More than 40,000 Israeli troops with hundreds of tanks entered Lebanon from three points: by land across the border into south Lebanon; by sea from the coast of Sidon; and by air as the Israeli forces bombed the Beqaa Valley, Beirut and its Palestinian refugee camps.
For two months, Beirut was under siege, with water and electricity cut off. As a result of the heavy bombardment and lack of access to basic needs, an estimated 19,000 Lebanese, Syrian and Palestinian civilians and combatants died, of which 5,500 were civilians from West Beirut.
The Lebanese authorities appealed to the United States, France, Italy and the United Kingdom for help. These countries formed the multinational peacekeeping force, which was designed to restore peace in Lebanon, assist the Lebanese armed forces and evacuate PLO fighters to Tunisia.
By August 1982, the multinational force had successfully relocated PLO fighters and began pulling out of Lebanon. They were called back, however, as violence flared.
After the assassination of Lebanese President-elect Bashir Gemayel on Sept. 14, 1982, the Christian Phalangist militia entered the two Palestinian refugee camps of Sabra and Shatila and killed over 2,000 Palestinian civilians. The Israeli government later set up the Kahan Commission of Inquiry to look into the killings, which concluded that Israel was indirectly responsible for the massacres.
The birth of Hezbollah
All of this history remains relevant to the current situation in the region. Israel’s invasion and occupation of Lebanon, its siege on Beirut and the massacres that followed all led to the birth of Hezbollah.
While members of Lebanon’s marginalized Shiite community in the south had long sought to mobilize through pan-Arab political parties and militias, it was Israel’s invasion that galvanized members of the community to ultimately create Hezbollah in 1985. As former Israeli Defense Minister and Prime Minister Ehud Barak noted in a 2006 interview: “It was our presence there that created Hezbollah.”
Israel’s invasion also soured Lebanon’s relations with the West. Many Lebanese and Palestinian Muslims considered the multinational force – especially the United States – to be a failure and even an accomplice to Israel.
From 1982 onward, Americans and other Westerners became a target. In the following decade, more than 80 Americans and Europeans were taken hostage by Hezbollah fighters. Some were tortured for months; others died in custody.
And on Oct. 23, 1983, a terrorist attack targeted the American barracks in Beirut, killing over 300 people, including 220 Marines, 18 sailors and three soldiers. Minutes later, a second suicide attack killed 58 French paratroopers. The Islamic Jihad claimed responsibility for the two attacks; some of its members are thought to be among those who officially founded Hezbollah in February 1985.
Aiding Hezbollah recruitment
Israel’s 1982 invasion of Lebanon failed to accomplish its goals of stemming attacks on Israel from southern Lebanon. If anything, it had the opposite effect by turning many Lebanese against Israel and creating the conditions in which Hezbollah could recruit.
Although Israel retreated from Beirut in August 1982, it continued to occupy south Lebanon until 2000. During that period it unlawfully detained many Lebanese suspected of resisting the Israeli occupation. Some were detained without charges in inhumane conditions, while others were illegally transferred into Israel.

Mahmoud Zayyat/AFP via Getty Images
With such a backdrop, Hezbollah’s legitimacy in the eyes of many Lebanese grew – as did its support. So much so that in 1989, at the end of the Lebanese civil war, the authorities signed an agreement that, although not referencing Hezbollah directly, asserted Lebanon’s right to resist the Israeli occupation in the south.
This clause was interpreted by Hezbollah as legitimizing its armed fight against occupation.
After occupation ended in 2000, Hezbollah had to reinvent its role, claiming that it would continue fighting against Israel until the liberation of the disputed Shebaa Farms, the Golan Heights and occupied Palestine.
In 2006, Hezbollah entered Israeli territory for the first time, killing three soldiers and kidnapping two, demanding the release of Lebanese prisoners in exchange. In retaliation, the Israel Defense Forces attacked Lebanon by air, sea and land, with Israeli ground forces entering Lebanon and carrying out a number of operations on Lebanese territory. A subsequent war saw no such prisoner swap but resulted in the deaths of about 1,100 Lebanese civilians and 120 Israelis, mostly soldiers.
History repeating?
Until Hamas attacked Israel on Oct. 7, 2023, there had been hopes that decades of hostilities between Lebanon and Israel could be on the cusp of turning. In October 2022, Lebanon and Israel signed a maritime border agreement brokered by the U.S – interpreted as the beginning of normalizing relations between two countries technically at war.
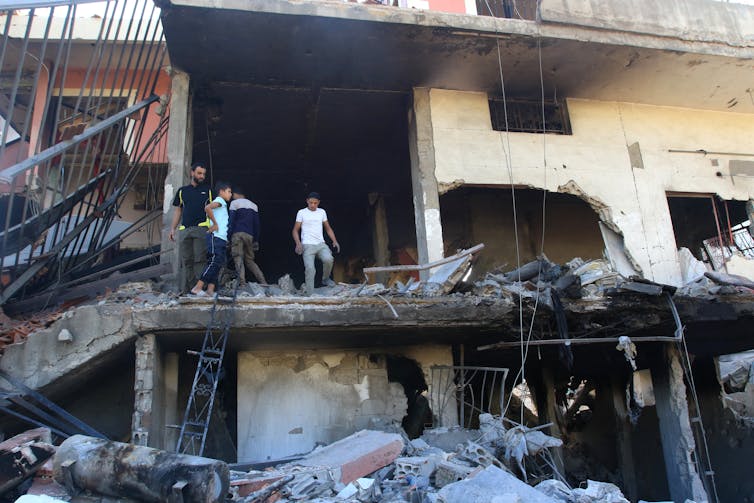
But the magnitude of the human crisis in Gaza and the series of events that followed in Lebanon have ended such hopes for now. Hezbollah’s vow of solidarity with Hamas has resulted in a running series of tit-for-tat attacks with Israel that have escalated over the past year.
The attack using booby-trapped pagers that targeted Hezbollah fighters and killed several civilians across Lebanon on Sept. 17, 2024, has set off a chain of events that have now seen nearly 500 Lebanese killed and Hezbollah extend the geographical scope of its missile attacks in Israel. Its long-range ballistic missiles can reach 250-300 kilometers (155-186 miles) and have reached Haifa and the city’s Ramat David Airbase.
The next step in this deadly escalation could well be a ground invasion. But in 1982, such an operation resulted only in catastrophic results for all concerned – and set in place the conditions for decades of hostilities across the Lebanon-Israel border. A similar offensive today would almost certainly have similar results – especially for the people of Lebanon.
![]()
Mireille Rebeiz is Chair of Middle East Studies & Associate Professor of Francophone & Women’s, Gender & Sexuality Studies at Dickinson College.




























Jake from state farm says
This may be a stupid question but why does the government of Lebanon allow Hezbollah to operate in their sovereign country? Iran seems to be controlling things in Lebanon.
Pierre Tristam says
Because the Lebanese government is a pathetic joke of corrupt tribal bosses. They were just as venal with the PLO. Hezbollah has them by the balls, which is why, the criminality of Israel’s indifference for civilian casualties, you won’t hear many Lebanese outside the Shiite south crying for the demise of Hezbollah leaders. Too bad Netanyahu and his gang aren’t any better. With Nasrallah’s assassination the so-called Lebanese government has a chance to seize the initiative and reassert its control over the south, possibly at the cost of another civil war (though nothing worse than what Netanyahu is causing), but it won’t. It’s incapable of doing the right thing.
Ray W says
Hello Mr. Tristam.
In the perhaps tortured fever dreams of the radical right’s American dystopian idealism, should they win by overthrowing the liberal democratic Constitutional Republic they so hate, the new government that emerges would likely parallel today’s now brutal and weak and divided Lebanon that was once a somewhat healthy government, back when Beirut and its beaches far below the heights were thought to be the “Paris of the Mediterranean.”
Beirut was once the playground of the Middle East. Oil money flowed through its many international banks. Nightclubs, hotels, restaurants, alcohol, casinos, mild weather patterns, and beautiful beaches — all magnetically drew the wealthy to the never-ending Arabian nightlife.
Then came the aftereffects of the Nakba. The fractious Sunni Palestinians had to go somewhere in 1948 or die. Hundreds of thousands settled in refugee camps or integrated into the fabric of Lebanese life. The relatively small Lebanese Shia faction that is the lifeblood of Hezbollah competed with the Palestinians for political power in central and south Lebanon.
We all know the rest. Palestinians, seeking hearth, home, family and security, repeatedly attacked Israel’s border posts. Israel invades in 1982, hoping to crush the Palestinians. Lebanese Shia leaders caught in between form Hezbollah.
Here is one reporter’s take on Hezbollah’s 1985 founding manifesto:
“[Hezbollah’s] aims were to drive the Israelis out of Lebanon and to eliminate the State of Israel – still a fundamental ambition today. It also aimed to oppose US ‘imperialism’, to spread the Iranian revolution, and to create an Islamist state in Lebanon – which has a substantial Christian population. Hezbollah has since softened the latter goal, unveiling a new document in 2009 that said the group supports ‘true democracy’. It still serves the interests of Iran, which the US says provides up to $700m a year in funding. But it has autonomy and its own specific aims; it should not be seen as a mere proxy.”
Make of this what you will. Me? The entire region holds to a primal version of the law of blood vengeance.
The 2500-year-old Oresteia, or the three plays of Agamemnon, is a commentary on the destruction of three royal generations wedded to the law of the debt of blood vengeance. The Greeks, horrified by the consequences of the law of the debt of blood vengeance, abolished the ancient or primal law and substituted justice in its place. They held the first recorded instance of a jury trial. Orestes was prosecuted by the Furies for matricide. Zeus defended him. A 12-person Athenian jury deadlocked 6-6. Athena stepped in to cast the deciding vote of not guilty, thereby introducing the concept of mercy into the law of justice.
Can it be argued that the peoples in the entire region comprising Lebanon and Palestine today are not yet sufficiently horrified enough to abolish their adherence to the ancient law of the debt of blood vengeance? That they are not yet ready to seek justice, tempered by mercy? That their ideal is for the rest of the world to leave them alone, so as to allow them to better thrash each other?
Many FlaglerLive commenters approach the violence spreading out of Gaza as if there is a way to win the argument. All of them are wrong. So long as the law of the debt of blood vengeance drives the violence, no one will ever win the argument. The only reasoned point is that the blood debt must continue to be paid, decade after decade, century after century, millennia after millennia, i.e., the thirst for blood cannot ever be slaked.
Pierre Tristam says
Ray, just as you were writing your comment I was writing a friend in a text, which I reproduce here: Now with the assassination of Hezbollah’s Nasrallah I find myself like most Lebanese (not from the Shiite South) simultaneously cheering his death, if that’s ever morally permissible, and condemning his killers. Nasrallah and Hezbollah have held Lebanon hostage just like the PLO before them. Nothing to redeem what they inflict on the country, especially after 2000, when Hezbollah achieved its objective of ending the Israeli occupation of the south. It could’ve crowned itself and stuck to politics. Instead it upped the savagery, against Israel and by sending its men to Syria to help Assad’s regime. Not men. Butchers. Plus they’re barbarically regressive. No one should mourn their loss. (The attack on the American and French barracks in October 1983 was there coming out). Not that without Nasrallah they won’t morph into something still more evil. The problem in Lebanon is always what comes next. It’s always worse. Always.
Jake from state farm says
Thanks for sharing this Pierre. It is good to here your view on this. But again, I have to say go back another step further and place some blame on where this all begins and is funded from. If you would do that your text to your friend would have been complete.
Jake from state farm says
Thanks for your reply Pierre. I do honestly always respect your view of what is going on there even if we disagree on the blame and solution. My comment is, if I am your neighbor and a group of thugs idiots funded by thugs in another city, comes and lives and your yard and throws rocks at my house and you do nothing, then I am going to do something to defend myself from the thugs. If you get in the way and allow the thugs to live in your yard, I am sorry but since you have given up, I suggest you just leave your house cause it’s going to get ugly. Instead of blaming me, the entire neighborhood, including you, should blame the thugs and the thugs in the city that’s funding them and encouraging them to throw rocks at me. That’s what is missing from all your posts, of course except for your brief comments on the radio. We won’t forget that aggressive put down of Iran. Until the problems of Iran using Hezbollah and the thugs in Gaza to throw rocks and use the innocents of Gaza and Lebanon as expendable fodder and sacrificial lambs, this never stops . You can blame Israel all you want but you need to blame who funds the rock throwing. Israel is not going to stop going after those who throw the rocks. If they hide in your house, I suggest get them out or move.
Pogo says
@Mireille Rebeiz is Chair of Middle East Studies & Associate Professor of Francophone & Women’s, Gender & Sexuality Studies at Dickinson College.
History repeating – you ask? Me too.
Working to repeat Dickinson College’s gift to American history?
As stated
“…Buchanan attended the Old Stone Academy in Mercersburg and then Dickinson College in Carlisle, Pennsylvania.[8] In 1808, he was nearly expelled for disorderly conduct; he and his fellow students had attracted negative attention for drinking in local taverns, disturbing the peace at night and committing acts of vandalism,[9] but he pleaded for a second chance and ultimately graduated with honors in 1809…”
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_Buchanan
Thanks for nothing, and less.
JC says
What Hez did to Former PM Hariri in 2005 was disgusting. Seems like after 2005 things went further downhill for the country.