
By Brian E. Roe
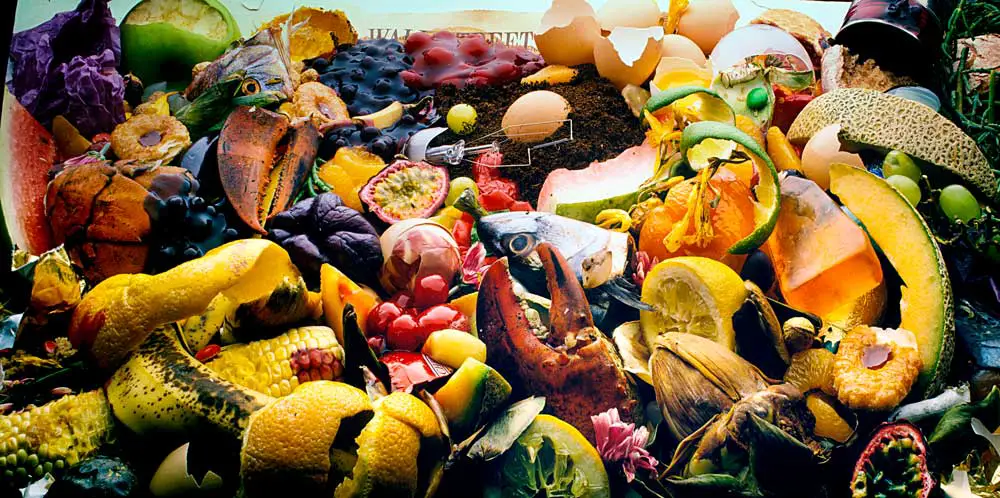
You saw it at Thanksgiving, and you’ll likely see it at your next holiday feast: piles of unwanted food – unfinished second helpings, underwhelming kitchen experiments and the like – all dressed up with no place to go, except the back of the refrigerator. With luck, hungry relatives will discover some of it before the inevitable green mold renders it inedible.
U.S. consumers waste a lot of food year-round – about one-third of all purchased food. That’s equivalent to 1,250 calories per person per day, or US$1,500 worth of groceries for a four-person household each year, an estimate that doesn’t include recent food price inflation. And when food goes bad, the land, labor, water, chemicals and energy that went into producing, processing, transporting, storing and preparing it are wasted too.
Where does all that unwanted food go? Mainly underground. Food waste occupies almost 25% of landfill space nationwide. Once buried, it breaks down, generating methane, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Recognizing those impacts, the U.S. government has set a goal of cutting food waste in half by 2030.
Reducing wasted food could protect natural resources, save consumers money, reduce hunger and slow climate change. But as an agricultural economist and director of the Ohio State Food Waste Collaborative, I know all too well that there’s no ready elegant solution. Developing meaningful interventions requires burrowing into the systems that make reducing food waste such a challenge for consumers, and understanding how both physical and human factors drive this problem.
Consumers and the squander sequence
To avoid being wasted, food must avert a gauntlet of possible missteps as it moves from soil to stomach. Baruch College marketing expert Lauren Block and her colleagues call this pathway the squander sequence.
It’s an example of what economists call an O-ring technology, harking back to the rubber seals whose catastrophic failure caused the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster in 1986. As in that event, failure of even a small component in the multistage sequence of transforming raw materials into human nutrition leads to failure of the entire task.
MIT economist Michael Kremer has shown that when corporations of many types are confronted with such sequential tasks, they put their highest-skilled staff at the final stages of production. Otherwise the companies risk losing all the value they have added to their raw materials through the production sequence.
Who performs the final stages of production in today’s modern food system? That would be us: frenzied, multitasking, money- and time-constrained consumers. At the end of a typical day, we’re often juggling myriad demands as we try to produce a nutritious, delicious meal for our households.
Unfortunately, sprawling modern food systems are not managed like a single integrated firm that’s focused on maximizing profits. And consumers are not the highly skilled heavy hitters that Kremer envisioned to manage the final stage of the complex food system. It’s not surprising that failure – here, wasting food – often is the result.
Indeed, out of everyone employed across the fragmented U.S. food system, consumers may have the least professional training in handling and preparing food. Adding to the mayhem, firms may not always want to help consumers get the most out of food purchases. That could reduce their sales – and if food that’s been stored longer degrades and becomes less appetizing or safe, producers’ reputations could suffer.
Three paths to squash the squandering
What options exist for reducing food waste in the kitchen? Here are several approaches.
- Build consumer skills.
This could start with students, perhaps through reinvesting in family and consumer science courses – the modern, expanded realm of old-school home economics classes. Or schools could insert food-related modules into existing classes. Biology students could learn why mold forms, and math students could calculate how to expand or reduce recipes.
Outside of school, there are expanding self-education opportunities available online or via clever gamified experiences like Hellman’s Fridge Night Mission, an app that challenges and coaches users to get one more meal a week out of their fridges, freezers and pantries. Yes, it may involve adding some mayo.
Recent studies have found that when people had the opportunity to brush up on their kitchen management skills early in the COVID-19 pandemic, food waste declined. However, as consumers returned to busy pre-COVID schedules and routines such as eating out, wastage rebounded.
- Make home meal preparation easier.
Enter the meal kit, which provides the exact quantity of ingredients needed. One recent study showed that compared to traditional home-cooked meals, wasted food declined by 38% for meals prepared from kits.
Meal kits generate increased packaging waste, but this additional impact may be offset by reduced food waste. Net environmental benefits may be case specific, and warrant more study.
- Heighten the consequences for wasting food.
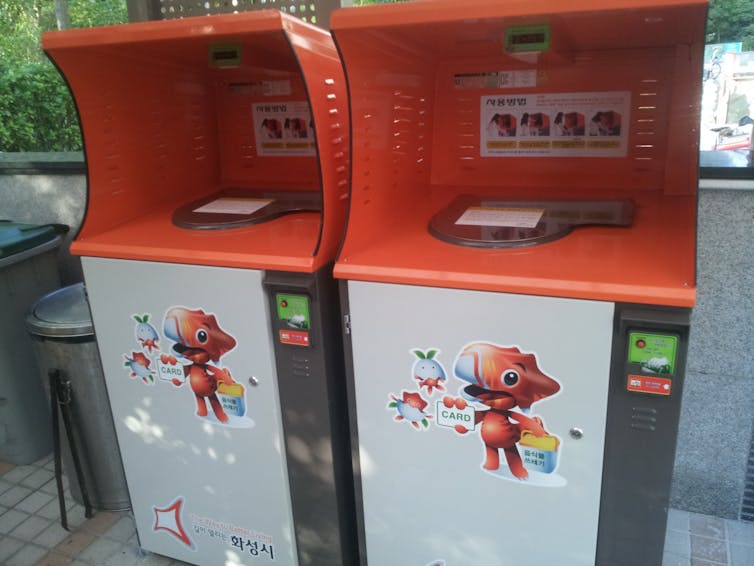
South Korea has begun implementing taxes on food wasted in homes by requiring people to dispose of it in special costly bags or, for apartment dwellers, through pay-as-you-go kiosks.

Revi/Wikipedia, CC BY
A recent analysis suggests that a small tax of 6 cents per kilogram – which, translated for a typical U.S. household, would total about $12 yearly – yielded a nearly 20% reduction in waste among the affected households. The tax also spurred households to spend 5% more time, or about an hour more per week, preparing meals, but the changes that people made reduced their yearly grocery bills by about $170.
No silver bullets
Each of these paths is promising, but there is no single solution to this problem. Not all consumers will seek out or encounter opportunities to improve their food-handling skills. Meal kits introduce logistical issues of their own and could be too expensive for some households. And few U.S. cities may be willing or able to develop systems for tracking and taxing wasted food.
As the National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine concluded in a 2020 report, there’s a need for many solutions to address food waste’s large contribution to global climate change and worldwide nutritional shortfalls. Both the United Nations and the U.S. National Science Foundation are funding efforts to track and measure food waste. I expect that this work will help us understand waste patterns more clearly and find effective ways to squelch the squander sequence.
![]()
Brian E. Roe is Professor of Agricultural, Environmental, and Development Economics at The Ohio State University.




























Laurel says
Um, guilty.
Good article with good suggestions. I would say start reducing dependence on processed foods. Good for the planet and good for your body to do so.
Also, really, really consider composting. It’s actually very easy. We had a small compost bin that we used for all uncooked plant based foods, shredded paper, cardboard, egg shells, coffee grinds, tea bags, and even dryer lint. No bones or meats, that’s another type of composting. Then, we got busy with a big project and forgot about composting. Later, the bin cracked so we threw it out leaving the composted pile on site. We tossed an alocasia bulb on the compost pile just to move it. You cannot imagine how big and beautiful that alocasia grew! You can save a lot on expensive potting soil, or garden soil, this way too! This stuff was way better than purchased potting soil. We’re getting another bin started soon!
Eat This says
I HATE it when some dork is going to tell me how to eat ,what to eat, when to eat. How much to buy, how much to throw out.
Listen up WOKENUTS, you eat your acorns and seaweed and leave me OUT of your socialist ways.