
By Alton C. Byers and Suzanne OConnell
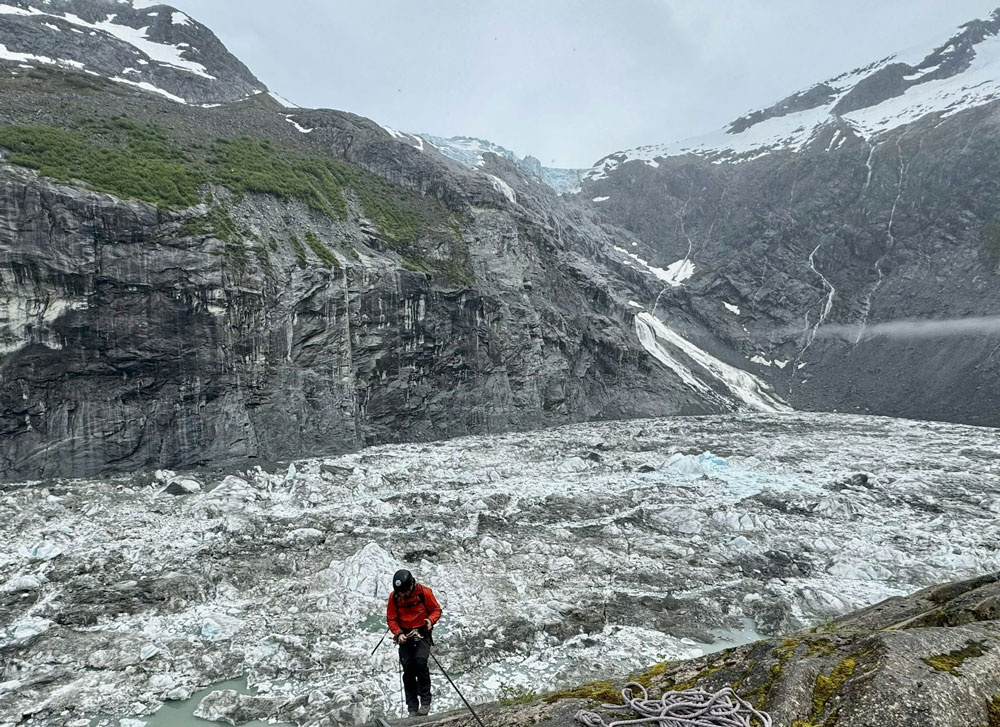
Each summer in the mountains above Juneau, Alaska, meltwater from the massive Mendenhall Glacier flows into mountain lakes and into the Mendenhall River, which runs through town.
Since 2011, scientists and local officials have kept a close eye on one lake in particular: Suicide Basin, an ice-dammed bowl on an arm of the glacier. Glacier ice once covered this area, but as the ice retreated in recent decades, it left behind a large, deep depression.
In the summers of 2023 and 2024, meltwater filled Suicide Basin, overflowed and escaped through tunnels in the ice, sending surges of water downstream that flooded neighborhoods along the river.
On Aug. 12-13, 2025, the basin flooded again.
The surge of water from Suicide Basin reached record levels at Mendenhall Lake on Aug. 13 on its way toward Juneau, the state capital. Officials urged some neighborhoods to evacuate ahead of the surge. As the water rose, new emergency flood barriers were able to limit the damage.
The glacial flood risks that Juneau is now experiencing each summer are becoming a growing problem in communities around the world. As an Earth scientist and a mountain geographer, we study the impact that ice loss can have on the stability of the surrounding mountain slopes and glacial lakes, and we see several reasons for increasing concern.

NOAA/Alaska Climate Adaptation Science Center
The growing risk of glacial floods
In many mountain ranges, glaciers are melting as global temperatures rise. Europe’s Alps and Pyrenees lost 40% of their glacier volume from 2000 to 2023.
These and other icy regions have provided freshwater for people living downstream for centuries – almost 2 billion people rely on glaciers today. But as glaciers melt faster, they also pose potentially lethal risks.
Water from the melting ice often drains into depressions once occupied by the glacier, creating large lakes. Many of these expanding lakes are held in place by precarious ice dams or rock moraines deposited by the glacier over centuries.

Alton Byers
Too much water behind these dams or a landslide or large ice discharge into the lake can break the dam, sending huge volumes of water and debris sweeping down the mountain valleys, wiping out everything in the way.
The Mendenhall Glacier floods, where glacial ice holds back the water, are classic jökulhlaup, or “glacier leap” floods, first described in Iceland and now characteristic of Alaska and other northern latitude regions.
Erupting ice dams and landslides
Most glacial lakes began forming over a century ago as a result of warming trends since the 1860s, but their abundance and rates of growth have risen rapidly since the 1960s.
Many people living in the Himalayas, Andes, Alps, Rocky Mountains, Iceland and Alaska have experienced glacial lake outburst floods of one type or another.
A glacial lake outburst flood in the Sikkim Himalayas in October 2023 damaged more than 30 bridges and destroyed a 200-foot-high (60 meters) hydropower plant. Residents had little warning. By the time the disaster was over, more than 50 people had died.
Avalanches, rockfalls and slope failures can also trigger glacial lake outburst floods.
These are growing more common as frozen ground known as permafrost thaws, robbing mountain landscapes of the cryospheric glue that formerly held them together. These slides can create massive waves when they plummet into a lake. The waves can then rupture the ice dam or moraine, unleashing a flood of water, sediment and debris.
That dangerous mix can rush downstream at speeds of 20-60 mph (30-100 kph), destroying homes and anything else in its path.
The casualties of such an event can be staggering. In 1941, a huge wave caused by a snow and ice avalanche that fell into Laguna Palcacocha, a glacial lake in the Peruvian Andes, overtopped the moraine dam that had contained the lake for decades. The resulting flood destroyed one-third of the downstream city of Huaraz and killed between 1,800 and 5,000 people.
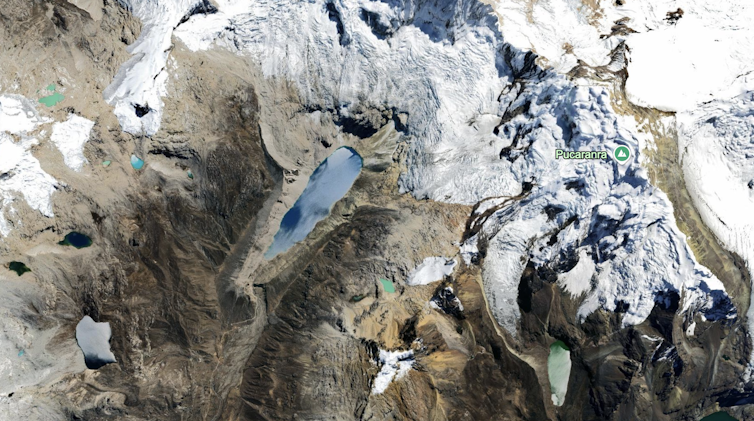

Google Earth, data from Airbus Data SIO, NOAA, U.S. Navy, NGA, GEBCO
In the years since, the danger there has only increased. Laguna Palcacocha has grown to more than 14 times its size in 1941. At the same time, the population of Huaraz has risen to over 120,000 inhabitants. A glacial lake outburst flood today could threaten the lives of an estimated 35,000 people living in the water’s path.
Governments have responded to this widespread and growing threat by developing early warning systems and programs to identify potentially dangerous glacial lakes. In Juneau, the U.S. Geological Survey starts monitoring Suicide Basin closely when it begins to fill.
Some governments have taken steps to lower water levels in the lakes or built flood-diversion structures, such as walls of rock-filled wire cages, known as gabions, that divert floodwaters from villages, infrastructure or agricultural fields.
Where the risks can’t be managed, communities have been encouraged to use zoning that prohibits building in flood-prone areas. Public education has helped build awareness of the flood risk, but the disasters continue.
Flooding from inside and thawing permafrost
The dramatic nature of glacial lake outburst floods captures headlines, but those aren’t the only risks.
Englacial conduit floods originate inside of glaciers, commonly on steep slopes. Meltwater can collect inside massive systems of ice caves, or conduits. A sudden surge of water from one cave to another, perhaps triggered by the rapid drainage of a surface pond, can set off a chain reaction that bursts out of the ice as a full-fledged flood.
Thawing mountain permafrost can also trigger floods. This permanently frozen mass of rock, ice and soil has been a fixture at altitudes above 19,685 feet (6,000 meters) for millennia.
As permafrost thaws, even solid rock becomes less stable and is more prone to breaking, while ice and debris are more likely to become detached and turn into destructive and dangerous debris flows. Thawing permafrost has been increasingly implicated in glacial lake outburst floods because of these new sources of potential triggers.
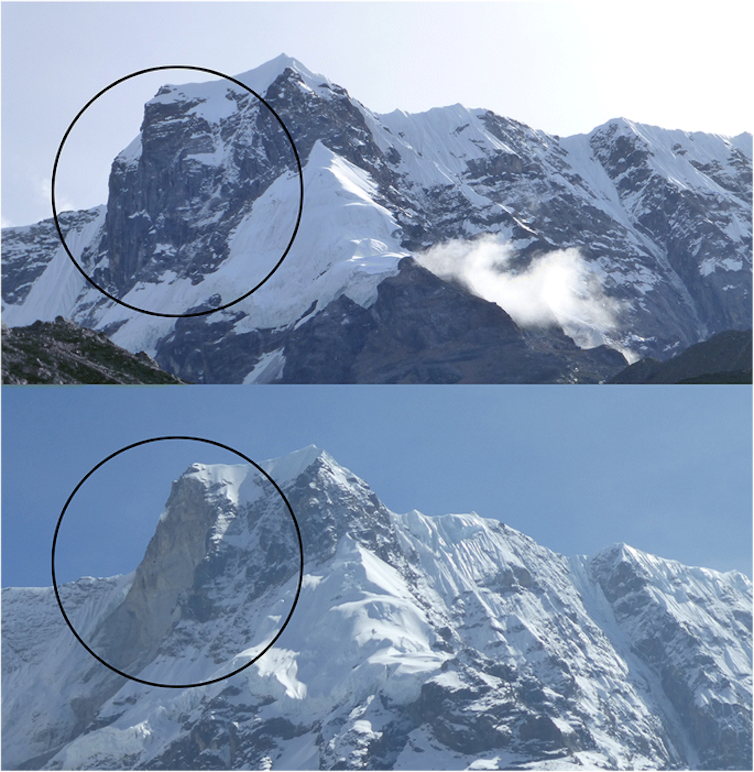

Elizabeth Byers (2016), Alton Byers (2017)
How mountain regions can reduce the risk
A study published in 2024 counted more than 110,000 glacial lakes around the world and determined 10 million people’s lives and homes are at risk from glacial lake outburst floods.
To help prepare and protect communities, our research points to some key lessons:
- Some of the most effective early warning systems have proven to be cellphone alerts. If combined with apps showing real-time water levels at a dangerous glacial lake, residents could more easily assess the danger.
- Projects to lower glacier lakes aren’t always effective. In the past, at least two glacial lakes in the Himalayas have been lowered by about 10 feet (3 meters) when studies indicated that closer to 65 feet (20 meters) was needed. In some cases, draining small, emerging lakes before they develop could be more cost effective than waiting until a large and dangerous lake threatens downstream communities.
- People living in remote mountain regions threatened by glacial lakes need a reliable source of information that can provide regular updates with monitoring technology.
- Recently it has become clear that even tiny glacial lakes can be dangerous given the right combination of cascading events. These need to be included in any list of potentially dangerous glacial lakes to warn communities downstream.
The U.N. declared 2025 the International Year of Glaciers’ Preservation and 2025-2034 the decade of action in cryospheric sciences. Scientists on several continents will be working to understand the risks and find ways to help communities respond to and mitigate the dangers.
![]()
Alton C. Byers is Faculty Research Scientist at the Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research at the University of Colorado Boulder. Suzanne OConnell is
Harold T. Stearns Professor of Earth Science at Wesleyan University.




























Pogo says
@News Notes Today: Galactic Council of Planets
… confirms murder/suicide of inhabitants of third rock from Sol; the signed affidavit of their ambassador, and recent deportee, Jesus, was received and recorded. The little rascals will be missed.
Maybe not.
Sherry says
Wait. . . this can’t be factual. . . some in the Maga brain trust commented previously (according to Fox?) that glaciers melting are the same as ice cubes melting in water. . . meaning that melting glaciers do not cause the oceans to rise or flooding. Climate change is just a hoax, right Maga? LOL! LOL! LOL!
Sadly, it’s not funny at all that so many US citizens are so uneducated, and that so many of the rest just don’t give a damn about the future of planet earth! trump VS Earth. . . they choose trump!