
By Erik Bleich and A. Maurits van der Veen
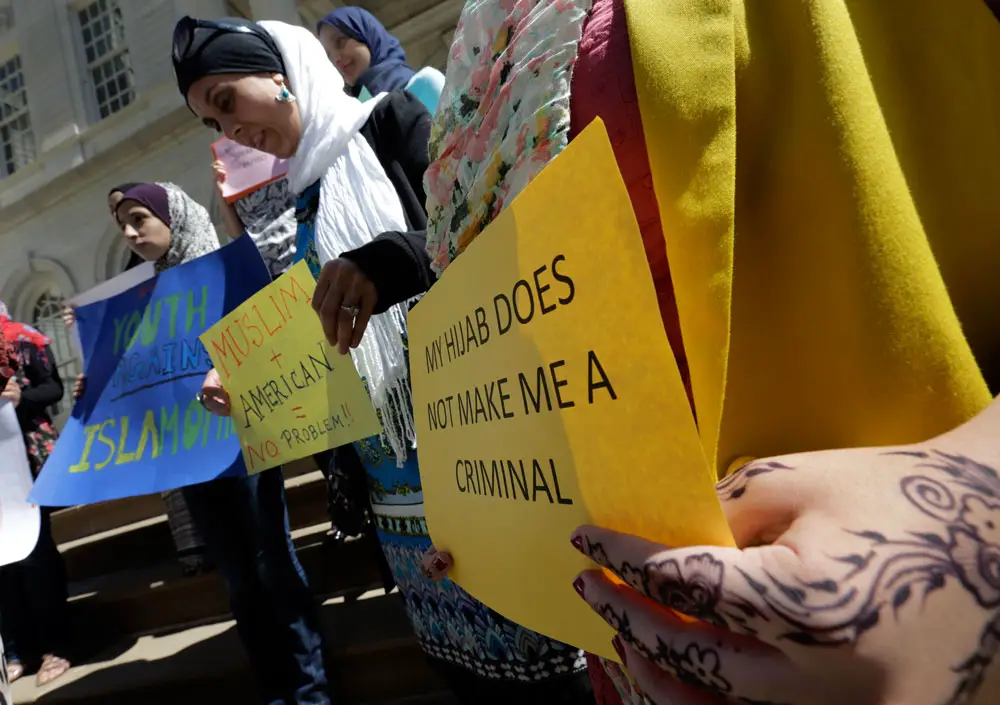
The warm welcome Americans and Europeans have given Ukrainians in 2022 contrasts sharply with the uneven – and frequently hostile – policies toward Syrian refugees in the mid-2010s.
Political scientist David Laitin has highlighted the role that religious identities play in this dynamic. As he pointed out in a recent interview, Syrian refugees were “mostly Muslim and faced higher degrees of discrimination than will the Ukrainians, who are largely of Christian heritage.”
The media provide information that shapes such attitudes toward Muslims. A 2007 Pew Research Center survey of Americans found that people’s negative opinions on Muslims were mostly influenced by what they heard and read in the media. Communications scholar Muniba Saleem and colleagues have demonstrated the link between media information and “stereotypic beliefs, negative emotions and support for harmful policies” toward Muslim Americans.
To better grasp the evolution of media portrayals of Muslims and Islam, our 2022 book, “Covering Muslims: American Newspapers in Comparative Perspective,” tracked the tone of hundreds of thousands of articles over decades.
We found overwhelmingly negative coverage, not only in the United States but also in the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia.
Negative coverage of Muslims
Previous research has identified widespread negative media representations of Muslims. An overview of studies undertaken from 2000 to 2015 by communications scholars Saifuddin Ahmed and Jörg Matthes concluded that Muslims were negatively framed in the media and that Islam was frequently cast as a violent religion.
But the studies they reviewed leave open two pressing questions that we address through our research.
First, do articles touching on Muslims and Islam include more negative representations than the average newspaper article? Second, are media portrayals of Muslims more negative than articles touching on other minority religions?
If stories about minority religious groups made it to the news only when they were involved in conflict in one way or another, then they may be negative for reasons that are not specific to Muslims.
What we found
To answer these questions, we used media databases such as LexisNexis, Nexis Uni, ProQuest and Factiva to download 256,963 articles mentioning Muslims or Islam – for which we use the shorthand “Muslim articles” – from 17 national, regional and tabloid newspapers in the United States over the 21-year period from Jan. 1, 1996, to Dec. 31, 2016.
We developed a reliable method for measuring the positivity or negativity of stories by comparing them to the tone of a random sample of 48,283 articles about topics drawn from a wide range of newspapers. A negative value on this scale means that a story is negative relative to the average newspaper article.
Crucially, this approach also provided a baseline for additional comparisons. We collected sets of articles from U.S. newspapers relating not only to Muslims, but also separately to Catholics, Jews and Hindus, three minority religious groups of varying size and status in the United States. We then assembled stories linked to Muslims from a broad array of newspapers in the U.K., Canada and Australia.
Our central finding is that the average article mentioning Muslims or Islam in the United States is more negative than 84% of articles in our random sample. This means that one would likely have to read six articles in U.S. newspapers to find even one that was as negative as the average article touching on Muslims.
To give a concrete sense of how negative typical Muslim articles are, consider the following sentence that has the tone of the average Muslim article: “The Russian was made to believe by undercover agents that the radioactive material was to be delivered to a Muslim organization.” This contains two highly negative words (“undercover” and “radioactive”) and implies that the “Muslim organization” has nefarious goals.
Articles that mentioned Muslims were also much more likely to be negative than stories touching on any other group we examined. For Catholics, Jews and Hindus, the proportion of positive and negative articles was close to 50-50. By contrast, 80% of all articles related to Muslims were negative.
The divergence is striking. Our work shows that the media are not prone to publishing negative stories when they write about other minority religions, but they are very likely to do so when they write about Muslims.
Beyond comparing coverage across groups, we were also interested in coverage across countries. Perhaps the United States is unique in its intensely negative coverage of Muslims. To find out, we collected 528,444 articles mentioning Muslims or Islam from the same time period from a range of newspapers in the U.K., Canada and Australia. We found that the proportion of negative to positive articles in these countries was almost exactly the same as that in the United States.
Implications of negative coverage
Multiple scholars have shown that negative stories generate less favorable attitudes toward Muslims. Other studies that looked at the impact of negative information about Muslims also found an increase in support for policies that harm Muslims, such as secret surveillance of Muslim Americans or the use of drone attacks in Muslim countries.
In addition, surveys of young American Muslims have found that negative media coverage resulted in weaker identification as American and in lower trust in the U.S. government.
We believe acknowledging and addressing the systemic negativity in media coverage of Muslims and Islam is vital for countering widespread stigmatization. This may, in turn, create opportunities for more humane policies that are fair to everyone regardless of their faith.
![]()
Erik Bleich is Charles A. Dana Professor of Political Science at Middlebury College, A. Maurits van der Veen is Associate Professor of Government at the College of William & Mary.




























Leave a Reply